September 2015 (Medical News Today)
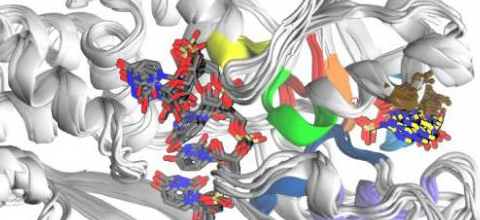
A team of scientists has created a computer simulation of an enzyme called NS3 that plays an important role in helping the hepatitis C virus replicate and spread in the body. The discovery should aid the search for drugs that uniquely target the virus.
To be able to target NS3, scientists need to know more about how it behaves. So far, the only knowledge has come from snapshots – still images – of the enzyme obtained through crystallography studies. The new computer simulation offers researchers the first ever opportunity to observe NS3 behavior as if watching a moving film.
Senior author Giovanni Bussi, professor and head of a SISSA group that makes computer simulations to study RNA, says their model reproduces the “interaction with ATP and subsequently with ADP, a waste product together with phosphate, after ATP had been utilized.” He concludes:
“By knowing in detail how this helicase works, in the future we could try to block the viral replication, and thus stop the disease from proliferating in the body.”